电池充电器原理
每次充电要根据电池化学成分按顺序施加电压和电流。因此,充电器和充电算法需满足不同电池化学成分的不同要求。电池充电常用术语包括:用于NiCd和NiMH电池的恒流(CC),和用于锂离子和锂聚合物电池的恒流/恒压(CC/CV) (图1至6)。
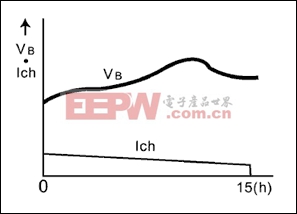
图1. 半恒流充电,主要应用于剃须刀,数字无绳电话和玩具
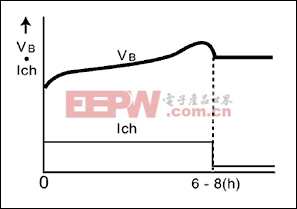
图2. 定时器控制充电,主要应用于笔记本,数据终端,无线设备和蜂窝电话
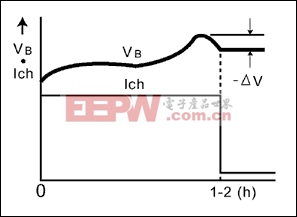
图3. -DV终止充电方式,主要应用于笔记本,数据终端,摄录像机,无线设备和蜂窝电话
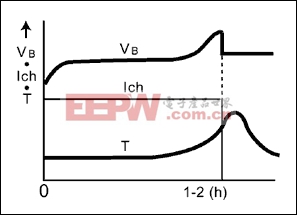
图4. -dT/dt终止充电方式,应用于电源设备和电动工具
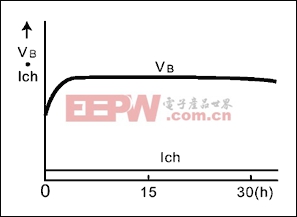
图5. 涓流充电,主要应用于应急灯,导引灯和存储器备份
表3. 充电方式
| Chemistry | Charging Method | Feature | No. of Terminals | Charge Time(hours) | Charge Current (CmA) | Trickle Current(CmA) | Charge Level at End of Charge (%) | Figure Reference |
| Nickel Based (NiCl and NiMH) | Semi-constant current charging | Most typical system; simple and low cost | 2 | 15 | 0,1 | ---- | ---- | 1 |
| Timer-controlled charging | More reliable than semiconstant current system; relatively simple and low cost | 2 | 6 to 8 | 0,2 | 1/20-1/30 | Approx. 120 | 2 | |
- V cut-off charging V cut-off charging | Most popular; more complex | 2 | 1 to 2 | 0,5-1 | 1/20-1/30 | Approx. 110 to 120 | 3 | |
 T/ T/ t cut-off charging t cut-off charging | More costly, but overcharge can be avoided enabling longer life cycle that the others | 3 or 4 | 1 to 2 | >1 | 1/20-1/30 | Approx. 100 to 110 | 4 | |
| Trickle-charging | Simple and low cost; applicable for continuous long charging | 2 | 15 | 0,1 | ---- | ---- | 5 | |
| Lithium Based | Constant current-constant voltage (CC-CV) | Not recommended for the main charge-control system for Ni-Cd /NiMH batteries. Prevailing charge method for Li+ and Li- Polymer batteries.Relatively complex charger design. | 2 | 1 to 3 | 1 | ---- | Approx 100 | 6 |
表4. 不同化学成分电池充满的判据
| Chemistry | NiCl | NiMH | Li+ |
| Charging | Constant current | Constant current | Constant current/constant voltage |
| Full charge detect | -
相关推荐技术专区 |










评论