WSNs中基于三因素节点评估的安全认证方案
(3)存储花费
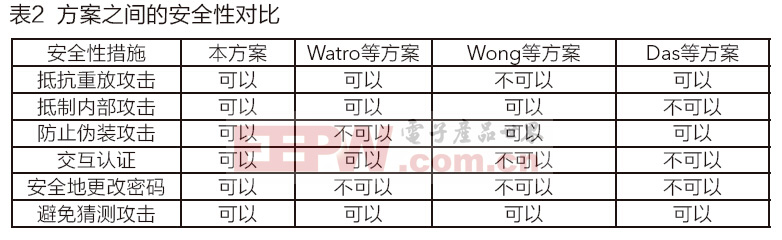
本文引用地址:https://www.eepw.com.cn/article/276364.htmWatro等提出的方案需要存储公/私密钥和系统参数,Wong等和Das等提出的方案需要存储系统参数,而本文提出的方案需要存储节点的信任度和系统参数,所以它需要占用更多的存储空间,图1给出了四个方案的传感器节点存储需求的比较。然而,随着传感器技术的不断提高,传感器节点的运算能力和存储能力都会有较大提升。
(4)节点能量花费
节点能量花费包括计算花费和通信花费。在Watro等提出的方案中,节点需要进行对用户请求的回复、随机数认证、检验和产生和确认以及两个公钥的运行。在Wong等提出的方案中,节点需要进行表查询、为产生参数而进行的哈希函数运算以及等待网关节点对用户请求的回复。在Das等提出的方案中,节点需要进行对用户请求的回复、时间戳认证以及为参数产生进行哈希运算。而在本文提出的方案中,节点会进行信任度计算、对用户请求的回复和时间戳认证。此方案减少了哈希运算的能量花费,而且通过信任度计算,大大提高认证过程的安全性。
3.3 仿真实验
为了评估这四种用户认证方案的有效性,本文在NS2的仿真环境下验证它们在有恶意节点的环境下用户成功认证的概率。设置参数如下:用户节点为15%,中继服务器节点为5%,节点射频通信距离为10,传感器节点的最大、最小个数为100,网络数目为400,执行数为100。注意,85%的节点是与用户认证的传感器节点。图2给出了仿真结果。从图中可以看出,相对于其他的三种用户认证方案,本文所提出的用户认证方案在有恶意节点的环境下仍保持了比较高的用户成功认证概率。
4 结语
无线传感器网络的认证技术在安全方面还存在很多的不足,同时还面临诸多的威胁。本文提出了一种无线传感器网络基于三因素节点评估的安全认证方案,它引入了时间片、安全行动系数和交互频度的轻量级的节点信任度计算方法,并与经过优化的认证方案相结合来进行用户认证。安全性分析、性能分析和仿真实验的结果表明,该方案有效地提高了节点所提供信息的真实性和准确性,并且与之前的许多认证方案相比,它具有更高的安全性,很适合无线传感器网络。通过该方案,平衡了整个过程的能量消耗,从而更好地应对针对无线传感器网络的安全攻击。未来的工作是进一步地完善该认证方案的性能,使其能够在无线传感器网络中得到广泛地应用。
参考文献:
[1]向亦宏, 朱燕民. 无线传感器网络中高效建立干扰模型的研究[J]. 计算机工程, 2014, 40(8): 1-5.
[2]Watro R, Kong D, Cuti S, et al. TinyPK: securing sensor networks with public key technology[C].Proceedings of the 2nd ACM workshop on Security of ad hoc and sensor networks. Washington,USA:ACM, 2004,59-64.
[3]Wong K H M, Zheng Yuan, Cao Jiannong, et al. A dynamic user authentication scheme for wireless sensor networks[C].Sensor Networks, Ubiquitous, and Trustworthy Computing.Taiwan: IEEE,2006,1-8.
[4]Das M L. Two-factor user authentication in wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Communications, IEEE Transactions on, 2009, 8(3): 1086-1090.
[5]Chen Tienho, Shih W K. A robust mutual authentication protocol for wireless sensor networks[J]. Etri Journal, 2010, 32(5): 704-712.
[6]Kumar P, Choudhury A J, Sain M, et al. RUASN: a robust user authentication framework for wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2011, 11(5): 5020-5046.
[7]Qi Aiqin, Shen Yongjun. An authentication protocol based on Chinese remainder theorem in wireless sensor networks[C].Conference Anthology, IEEE. Lanzhou,China:IEEE, 2013,1-3.
[8]马力,郑国宁,孙朋.节点信任度模型的算法研究设计[J].计算机科学,2012, 39(B06): 81-85.
[9]Gu Chengjie, Zhang Shunyi, Feng Huibin, et al. A novel trust management model for P2P network with reputation and risk evaluation[C].E-Business and E-Government (ICEE).Nanjing,China:IEEE,2010,3544-3547.
[10]Wu Guowei, Du Zhuang, Hu Yibo, et al. A dynamic trust model exploiting the time slice in WSNs[J]. Soft Computing, 2014, 18(9): 1829-1840.
[11]Messerges T S, Dabbish E A, Sloan R H. Examining smart-card security under the threat of power analysis attacks[J]. Computers, IEEE Transactions on, 2002, 51(5): 541-552.
[12]Shah M D, Gala S N, Shekokar N M. Lightweight authentication protocol used in Wireless Sensor Network[C].Circuits, Systems, Communication and Information Technology Applications (CSCITA).Mumbai,India:IEEE,,2014:,138-143.
[13]Delgado-Mohatar O, Fúster-Sabater A, Sierra J M. A light-weight authentication scheme for wireless sensor networks[J].Ad Hoc Networks, 2011, 9(5): 727-735.
[14]Yu Yanli, Li Keqiu, Zhou Wanlei, et al. Trust mechanisms in wireless sensor networks: Attack analysis and countermeasures[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications,2012,35(3): 867-880.
[15]Lee C C, Hsu C W. A secure biometric-based remote user authentication with key agreement scheme using extended chaotic maps[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2013, 71(1-2): 201-211.
















评论