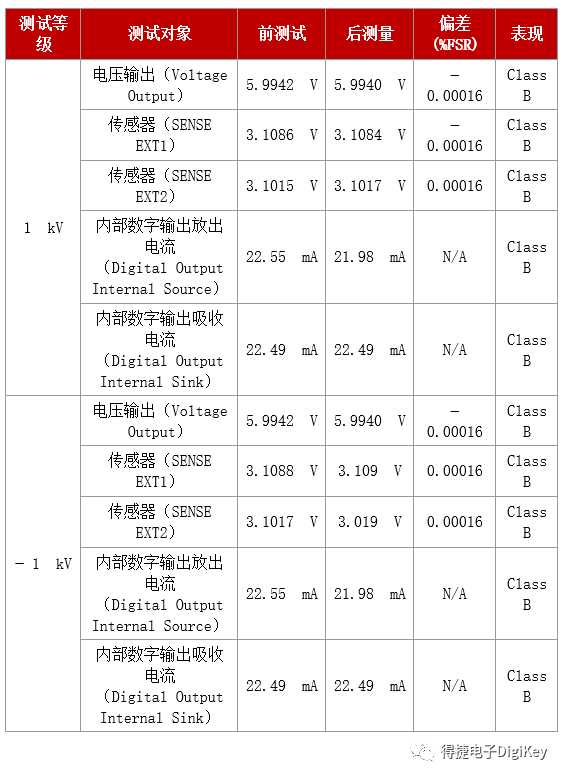
8/20浪涌测试波形时域转频域的解释及仿真思路(基于Python)
1.引言
在电子工程和电磁兼容性(EMC)领域,8/20μs浪涌波形是一种标准的感应雷,常用于模拟雷电引起的瞬态过电流。这个波形因其陡峭的上升沿(8μs)和较长的下降沿(20μs)而得名,能够很好地模拟雷电冲击对电子设备的影响。今天,我将带领大家一步步了解如何通过仿真分析8/20μs浪涌波形的时域特性,并将其转换到频域进行分析,揭示其频率成分。2.时域分析
2.1 8/20μs浪涌波形的定义
8/20μs浪涌波形是一种典型的双指数脉冲波形,其数学表达式可以表示为:

其中:


这个公式看起来有点复杂,但其实就是在两个指数函数之间做差,从而得到一个脉冲波形。简单来说,就是用一个快速下降的指数函数减去一个更慢下降的指数函数,形成一个快速上升、缓慢下降的脉冲。
2.2仿真生成时域波形
在代码中,`generate_8_20_waveform`函数通过上述公式生成8/20μs浪涌波形。具体步骤如下:
1.使用`np.linspace`生成时间数组`time`,表示仿真时间范围。
2.计算电流波形`current`,使用双指数函数模拟上升沿和下降沿。
3.对波形进行归一化处理,确保峰值电流为4kA。
生成的时域波形,展示了8/20μs浪涌波形的典型特性。
3.频域分析
3.1时域到频域的转换
为了分析8/20μs浪涌波形的频率成分,需要将其从时域转换到频域。这一过程可以通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)实现。FFT的基本原理是将时域信号分解为不同频率成分的叠加,从而得到信号的频谱。
在代码中,`analyze_frequency_domain`函数使用`scipy.fft.fft`计算信号的频域表示。具体步骤如下:
1.计算信号的FFT,得到复数频谱。
2.提取频率数组`freq`和幅度谱`magnitude`。
3.对幅度谱进行归一化处理,使其单位为“kA/Hz”。
3.2频域波形的特性
8/20μs浪涌波形的频域特性可以通过其频谱图进行分析。由于该波形是一个瞬态脉冲,其频谱通常呈现宽带特性,包含从低频到高频的成分。
在代码中,频域波形以对数-对数(log-log)尺度绘制。频谱图展示了信号在不同频率下的幅度分布。通过频谱图可以观察到:
-信号在低频段(如1MHz以下)具有较高的幅度。
-随着频率的增加,幅度逐渐减小,但仍然包含高频成分。
3.3频域分析的意义
频域分析对于理解8/20μs浪涌波形的特性具有重要意义:
1.频谱特性:频域分析可以揭示信号在不同频率下的能量分布,有助于设计滤波器或保护电路。
2.电磁兼容性:通过频域分析,可以评估信号对其他设备的干扰特性,从而优化电磁兼容性设计。
3.实际应用:频域特性可以用于验证设备在不同频率下的抗干扰能力。
4.仿真思路总结
4.1仿真流程
1.时域波形生成:
-使用双指数函数生成8/20μs浪涌波形。
-确保波形的峰值电流为4kA。
2.频域分析:
-使用FFT将时域信号转换为频域信号。
-计算频率数组和幅度谱。
3.结果可视化:
-绘制时域波形图,展示8/20μs浪涌波形的时域特性。
-绘制频域波形图,展示信号的频谱特性。
4.2仿真结果分析
通过仿真可以得到以下结论:
-8/20μs浪涌波形在时域上表现为一个快速上升、缓慢下降的脉冲。
-在频域上,该波形呈现宽带特性,包含从低频到高频的成分。
-频域分析可以为电磁兼容性设计和滤波器设计提供重要参考。
5.结论
通过对8/20μs浪涌波形的时域和频域分析,可以全面理解其特性及其对电子设备的影响。时域分析揭示了波形的瞬态特性,而频域分析则揭示了其频率成分。这种分析方法对于设计抗干扰电路和优化电磁兼容性具有重要意义。
通过本文的仿真思路和代码实现,进一步探索8/20μs浪涌波形的特性,并将其应用于实际工程中。希望这篇文章能帮助大家更好地理解8/20μs浪涌波形的时域转频域分析,同时也希望大家在学习过程中能够保持好奇心和探索精神,不断进步!

附代码:
1. import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.fft import fft, fftfreq
#import B-tron EMC
# Set font to support English display
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["DejaVu Sans", "Arial", "sans-serif"]
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False # Ensure minus sign display
def generate_8_20_waveform(duration=100e-6, samples=10000):
"""
Generate 8/20μs standard lightning impulse current waveform
Parameters:
duration: Simulation duration (seconds)
samples: Number of sampling points
Returns:
time: Time array (seconds)
current: Current array (kA)
"""
t = np.linspace(0, duration, samples)
# 8/20μs waveform parameters
tau1 = 8e-6 # Front time constant
tau2 = 20e-6 # Tail time constant
amplitude = 4 # Amplitude (kA)
# Calculate current waveform (exponential decay model)
current = amplitude * (np.exp(-t / tau2) - np.exp(-t / tau1))
# Normalize to make peak value 4kA
current = current / np.max(current) * amplitude
return t, current
def analyze_frequency_domain(time, signal, sampling_freq):
"""
Perform frequency domain analysis
Parameters:
time: Time array (seconds)
signal: Signal array
sampling_freq: Sampling frequency (Hz)
Returns:
freq: Frequency array (Hz)
magnitude: Amplitude spectrum
"""
n = len(signal)
yf = fft(signal)
freq = fftfreq(n, 1 / sampling_freq)[:n // 2]
magnitude = 2.0 / n * np.abs(yf[:n // 2])
return freq, magnitude
def plot_waveforms(time, current, freq, magnitude):
"""Plot time-domain and frequency-domain waveforms"""
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(10, 10))
# Time-domain waveform
ax1.plot(time * 1e6, current) # Convert time to μs
ax1.set_title('8/20μs Lightning Impulse Current Waveform (Time Domain)')
ax1.set_xlabel('Time (μs)')
ax1.set_ylabel('Current (kA)')
ax1.grid(True)
# Mark peak value and time parameters
peak_idx = np.argmax(current)
t_peak = time[peak_idx] * 1e6
ax1.annotate(f'Peak: {current[peak_idx]:.2f} kA\nTime: {t_peak:.2f} μs',
xy=(t_peak, current[peak_idx]),
xytext=(t_peak + 5, current[peak_idx] * 0.8),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
# Frequency-domain waveform (log-log scale)
ax2.loglog(freq, magnitude)
ax2.set_title('Frequency Spectrum of 8/20μs Lightning Impulse Current')
ax2.set_xlabel('Frequency (MHz)')
ax2.set_ylabel('Magnitude (kA/Hz)')
ax2.grid(True, which='both', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
# Add spectral feature annotations
freq_1MHz = np.interp(1e6, freq, magnitude)
freq_10MHz = np.interp(1e7, freq, magnitude)
ax2.annotate(f'1 MHz: {freq_1MHz:.2e} kA/Hz',
xy=(1e6, freq_1MHz),
xytext=(1e6 * 2, freq_1MHz * 3),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
ax2.annotate(f'10 MHz: {freq_10MHz:.2e} kA/Hz',
xy=(1e7, freq_10MHz),
xytext=(1e7 * 2, freq_10MHz * 3),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
plt.tight_layout()
return fig
def main():
# Generate 8/20μs waveform
time, current = generate_8_20_waveform(duration=100e-6, samples=10000)
# Calculate sampling frequency
sampling_freq = len(time) / (time[-1] - time[0])
# Frequency domain analysis
freq, magnitude = analyze_frequency_domain(time, current, sampling_freq)
# Plot waveforms
fig = plot_waveforms(time, current, freq, magnitude)
# Display waveforms
plt.show()
# Print magnitude at key frequencies
print("8/20μs Waveform Frequency Characteristics:__B-tron")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
*博客内容为网友个人发布,仅代表博主个人观点,如有侵权请联系工作人员删除。