树莓派RP2350-桌面动态温湿度计
本文介绍了DFRobot Beetle RP2350开发板结合DHT11模块、锂电池模块、随机眨眼动画,实现OLED 显示的桌面动态温湿度计的项目设计。
2 项目介绍
本项目包括如下。
工作原理:ADC电压采集与电量转换
工程调试:电量获取、电量图标显示、DHT11温湿度显示、OLED眨眼动画
工程代码:合并调试代码,实现完整的项目设计功能
效果演示:帧动画显示、动态展示
最终实现桌面动态温湿度计的制作。
3 工作原理
根据开发板原理图可知,电池VBAT的分压电路与主控的GPIO29模拟接口相连,因此通过该引脚可实时采集监测电池电压信息,进而实现电量显示。
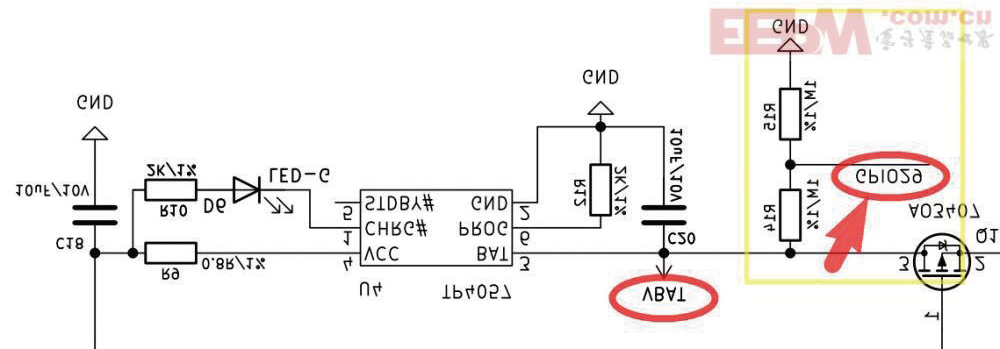
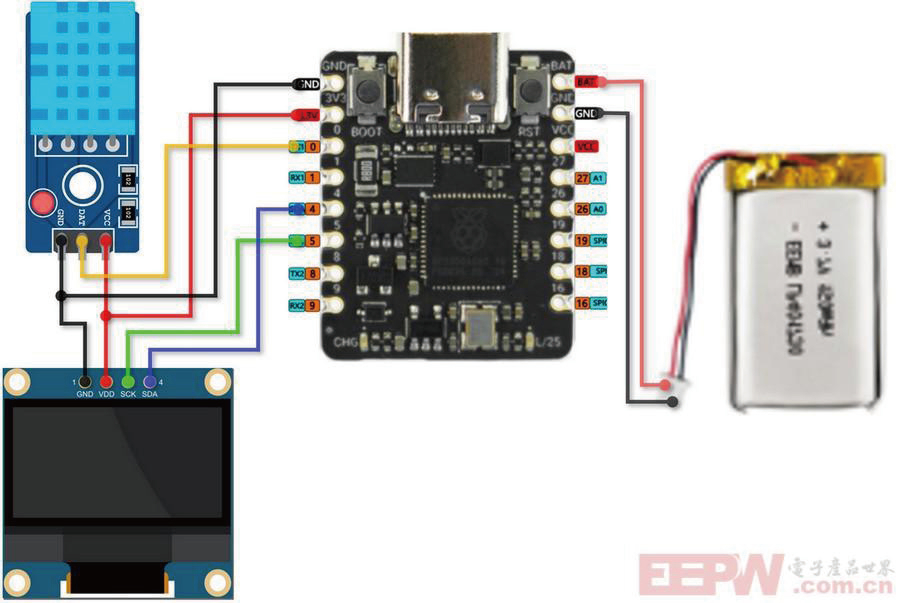
4 硬件连接
GP0->DATA(DHT11)
GP4->SDA(OLED)
GP5->SCL(OLED)
BAT->Battery Positive
GND->Battery Negative
5 示意图
6 工程调试
包括ADC电量采集、电量的OLED显示、DHT11温湿度数据和电量图标的显示、眨眼动画等调试项目。
7 电量获取
通过ADC 读取GPIO29 电压值并终端打印
8 代码


保存代码,连接开发板,配置解释器并运行。
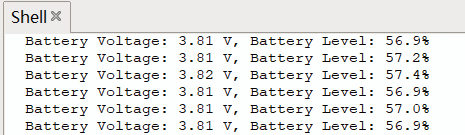
9 效果
终端打印ADC 采集的电池电压值以及电量百分比
10 电量显示
OLED显示ADC采集的电量百分比。
11 代码



保存代码,连接开发板,配置解释器并运行。
12 效果
电量图标的水平显示
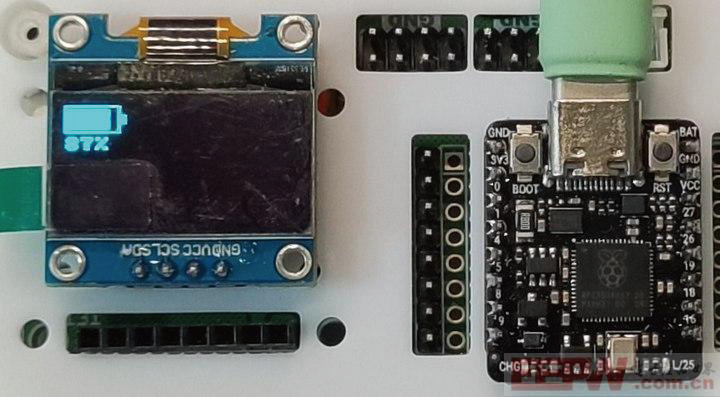
电量图标的竖直显示
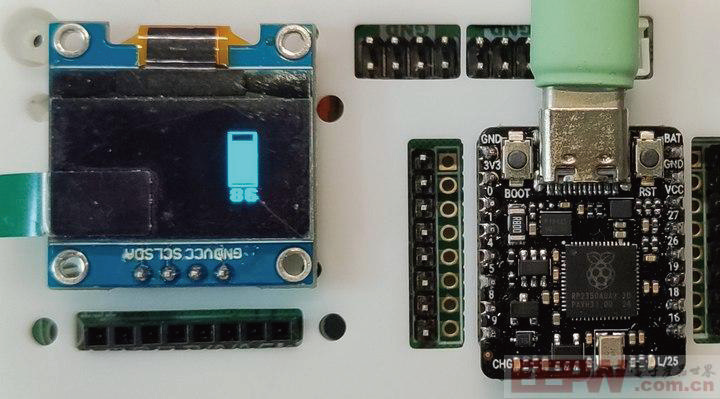
13 DHT11温湿度计
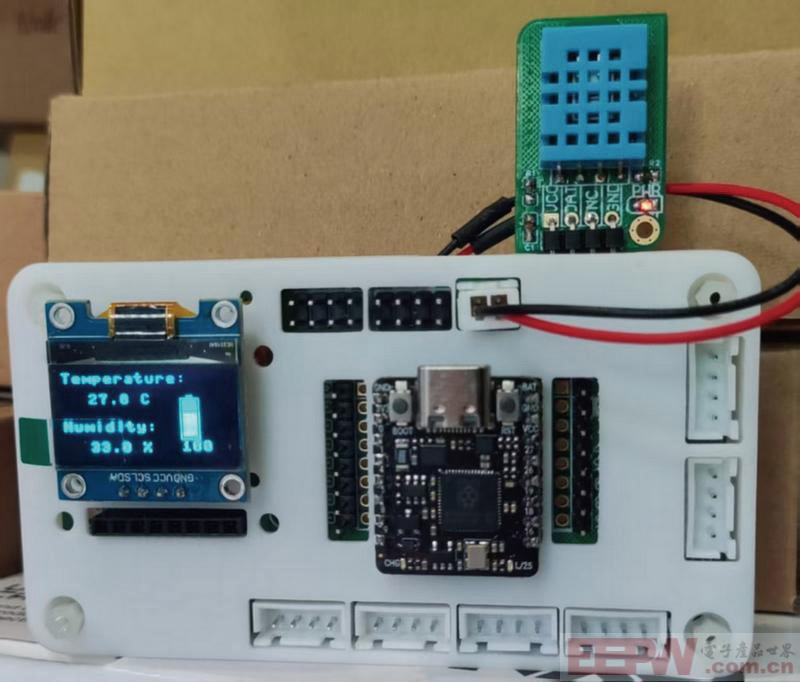
带电量显示的DHT11温湿度计
14 代码



15 效果
电量和温湿度显示,数据刷新的时间间隔为2秒
16 眨眼动画
OLED显示矩形填充状眼睛,改变形状并利用人眼的视觉暂留效应实现眨眼效果。
17 代码



保存代码,连接开发板,配置解释器并运行。
18 效果
眨眼效果(眼睛位置在屏幕内随机移动)

19 工程代码
将工程调试的代码合并,实现温湿度数据(包括电池电量)与息屏随机眨眼动画的切换显示。





连接开发板,配置解释器,将代码保存至根目录,取下数据线,连接电池,实现显示效果。
20 效果
帧动画分别如下
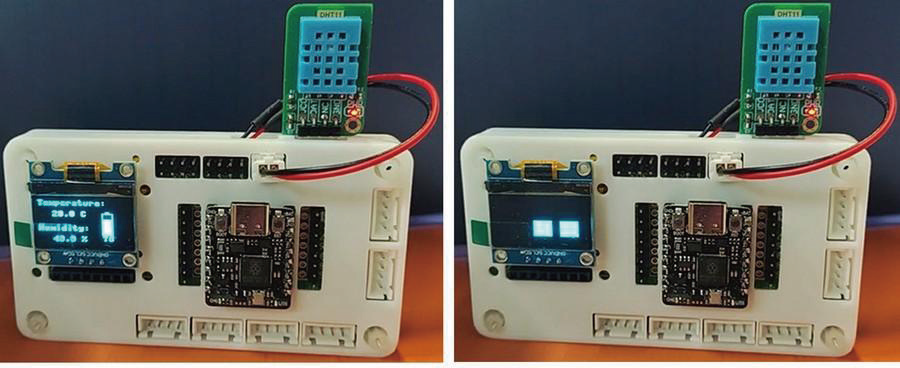
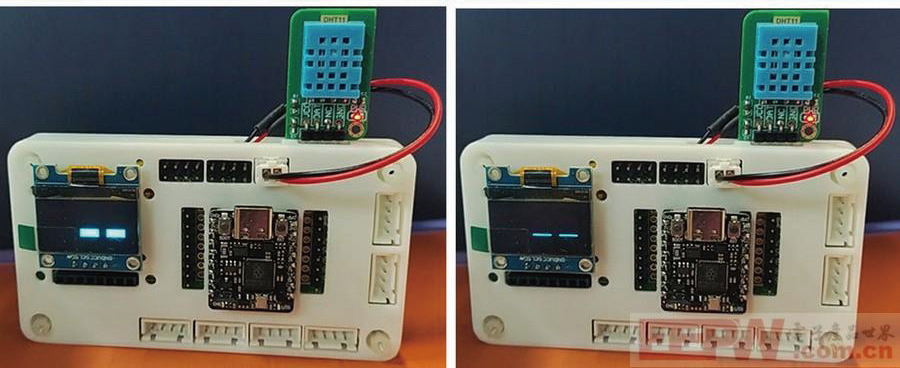
21 总结
本文介绍了树莓派RP2350开发板结合DHT11模块、锂电池模块、随机眨眼动画,实现OLED显示的桌面动态温湿度计的项目设计。通过多任务结合,为更多DIY设计提供了可能,如添加按键扫描或语音控制模块,实现指定的功能切换与人机交互,拓展和丰富了该开发板在物联网领域的创新与应用,为RP2350 的开发设计和产品应用提供了参考。
(本文来源于《EEPW》202506)








评论