多线程编程之:Linux线程编程
9.2.3 线程属性
本文引用地址:http://www.eepw.com.cn/article/264053.htm(1)函数说明。
pthread_create()函数的第二个参数(pthread_attr_t *attr)表示线程的属性。在上一个实例中,将该值设为NULL,也就是采用默认属性,线程的多项属性都是可以更改的。这些属性主要包括绑定属性、分离属性、堆栈地址、堆栈大小以及优先级。其中系统默认的属性为非绑定、非分离、缺省1M的堆栈以及与父进程同样级别的优先级。下面首先对绑定属性和分离属性的基本概念进行讲解。
n 绑定属性。
前面已经提到,Linux中采用“一对一”的线程机制,也就是一个用户线程对应一个内核线程。绑定属性就是指一个用户线程固定地分配给一个内核线程,因为CPU时间片的调度是面向内核线程(也就是轻量级进程)的,因此具有绑定属性的线程可以保证在需要的时候总有一个内核线程与之对应。而与之对应的非绑定属性就是指用户线程和内核线程的关系不是始终固定的,而是由系统来控制分配的。
n 分离属性。
分离属性是用来决定一个线程以什么样的方式来终止自己。在非分离情况下,当一个线程结束时,它所占用的系统资源并没有被释放,也就是没有真正的终止。只有当pthread_join()函数返回时,创建的线程才能释放自己占用的系统资源。而在分离属性情况下,一个线程结束时立即释放它所占有的系统资源。这里要注意的一点是,如果设置一个线程的分离属性,而这个线程运行又非常快,那么它很可能在pthread_create()函数返回之前就终止了,它终止以后就可能将线程号和系统资源移交给其他的线程使用,这时调用pthread_create()的线程就得到了错误的线程号。
这些属性的设置都是通过特定的函数来完成的,通常首先调用pthread_attr_init()函数进行初始化,之后再调用相应的属性设置函数,最后调用pthread_attr_destroy()函数对分配的属性结构指针进行清理和回收。设置绑定属性的函数为pthread_attr_setscope(),设置线程分离属性的函数为pthread_attr_setdetachstate(),设置线程优先级的相关函数为pthread_attr_getschedparam()(获取线程优先级)和pthread_attr_setschedparam()(设置线程优先级)。在设置完这些属性后,就可以调用pthread_create()函数来创建线程了。
(2)函数格式。
表9.9列出了pthread_attr_init()函数的语法要点。
表9.10列出了pthread_attr_setscope()函数的语法要点。
表9.11列出了pthread_attr_setdetachstate()函数的语法要点。
表9.12 pthread_attr_getschedparam()函数语法要点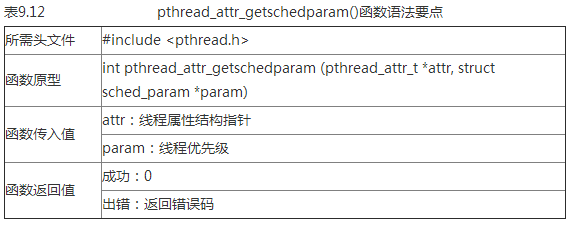
表9.13列出了pthread_attr_setschedparam()函数的语法要点。
(3)使用实例。
下面的实例是在我们已经很熟悉的实例的基础上增加线程属性设置的功能。为了避免不必要的复杂性,这里就创建一个线程,这个线程具有绑定和分离属性,而且主线程通过一个finish_flag标志变量来获得线程结束的消息,而并不调用pthread_join()函数。
/*thread_attr.c*/
#include
#include
#include
#define REPEAT_NUMBER 3 /* 线程中的小任务数 */
#define DELAY_TIME_LEVELS 10.0 /* 小任务之间的最大时间间隔 */
int finish_flag = 0;
void *thrd_func(void *arg)
{
int delay_time = 0;
int count = 0;
printf("Thread is startingn");
for (count = 0; count < REPEAT_NUMBER; count++)
{
delay_time = (int)(rand() * DELAY_TIME_LEVELS/(RAND_MAX)) + 1;
sleep(delay_time);
printf("tThread : job %d delay = %dn", count, delay_time);
}
printf("Thread finishedn");
finish_flag = 1;
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t thread;
pthread_attr_t attr;
int no = 0, res;
void * thrd_ret;
srand(time(NULL));
/* 初始化线程属性对象 */
res = pthread_attr_init(&attr);
if (res != 0)
{
printf("Create attribute failedn");
exit(res);
}
/* 设置线程绑定属性 */
res = pthread_attr_setscope(&attr, PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM);
/* 设置线程分离属性 */
res += pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
if (res != 0)
{
printf("Setting attribute failedn");
exit(res);
}
res = pthread_create(&thread, &attr, thrd_func, NULL);
if (res != 0)
{
printf("Create thread failedn");
exit(res);
}
/* 释放线程属性对象 */
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
printf("Create tread successn");
while(!finish_flag)
{
printf("Waiting for thread to finish...n");
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}
接下来可以在线程运行前后使用“free”命令查看内存的使用情况。以下是运行结果:
$ ./thread_attr
Create tread success
Waiting for thread to finish...
Thread is starting
Waiting for thread to finish...
Thread : job 0 delay = 3
Waiting for thread to finish...
Thread : job 1 delay = 2
Waiting for thread to finish...
Waiting for thread to finish...
Waiting for thread to finish...
Waiting for thread to finish...
Thread : job 2 delay = 9
Thread finished
/* 程序运行之前 */
$ free
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 255556 191940 63616 10 5864 61360
-/+ buffers/cache: 124716 130840
Swap: 377488 18352 359136
/* 程序运行之中 */
$ free
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 255556 191948 63608 10 5888 61336
-/+ buffers/cache: 124724 130832
Swap: 377488 18352 359136
/* 程序运行之后 */
$ free
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 255556 191940 63616 10 5904 61320
-/+ buffers/cache: 124716 130840
Swap: 377488 18352 359136
可以看到,线程在运行结束后就收回了系统资源,并释放内存。
linux操作系统文章专题:linux操作系统详解(linux不再难懂)linux相关文章:linux教程
尘埃粒子计数器相关文章:尘埃粒子计数器原理













评论